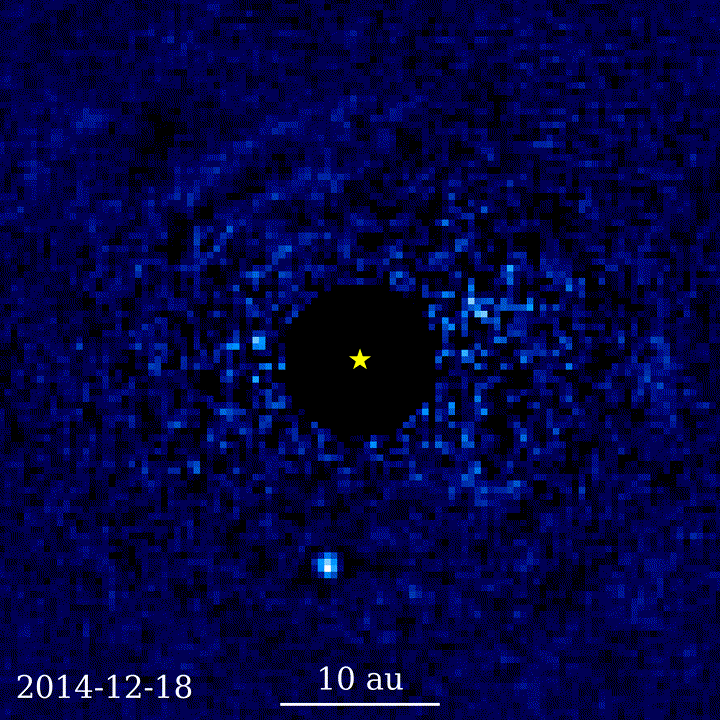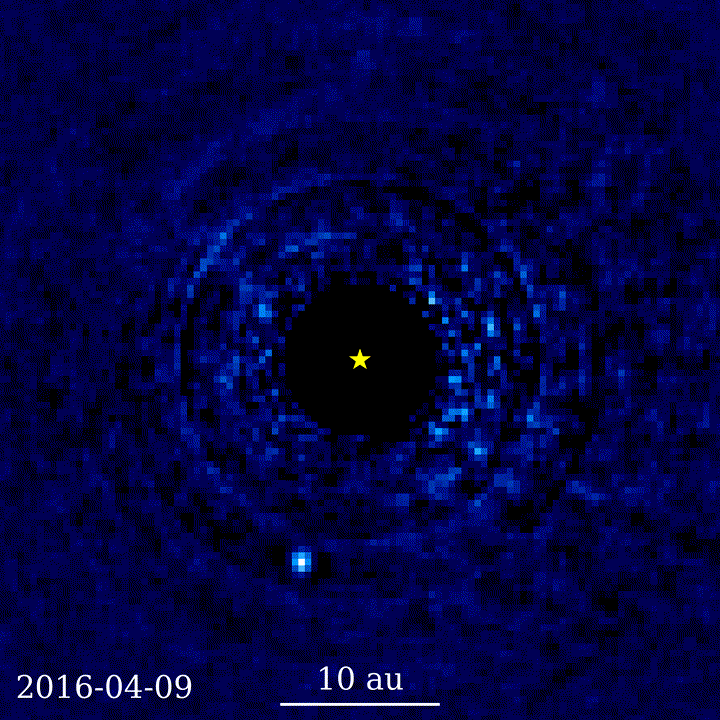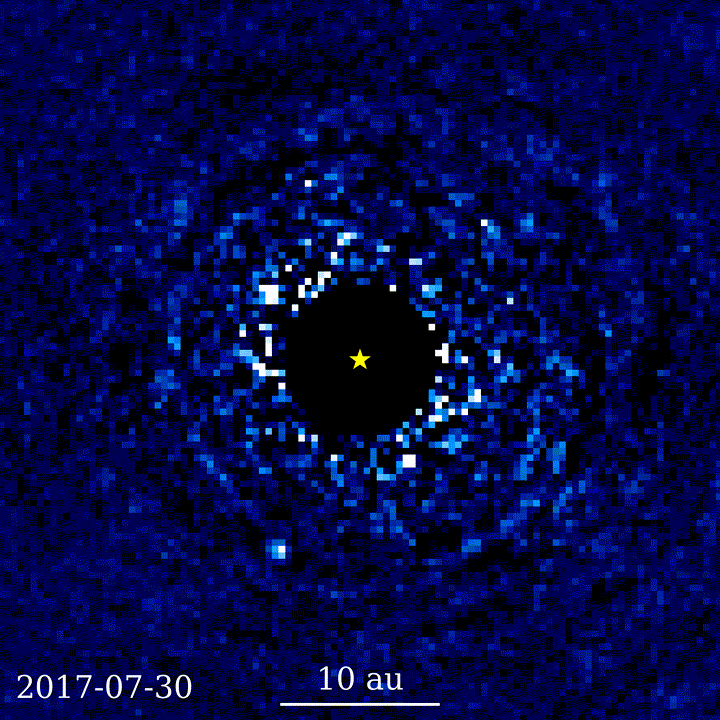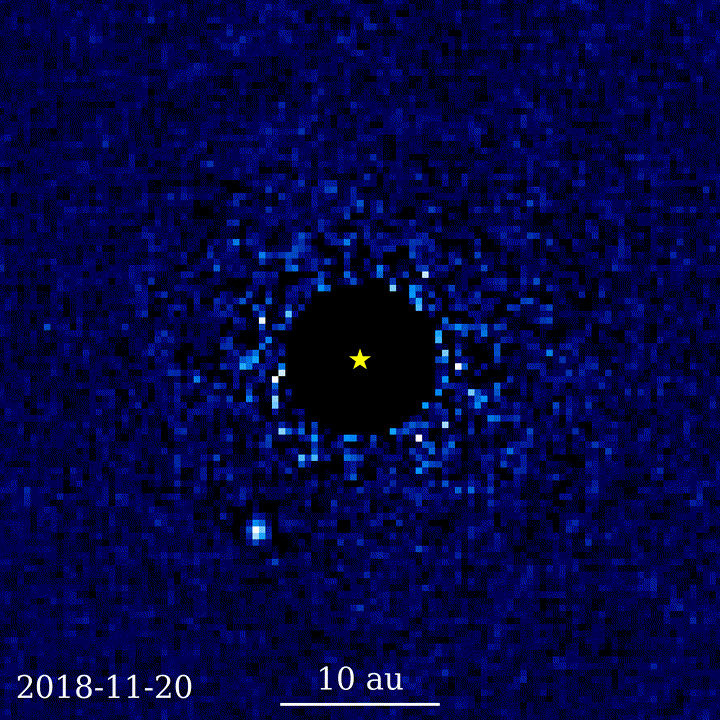
Challenges with seeing distant objects through telescopes
Countless wishes have been made on a twinkling star.
Ironically, that twinkle is one thing that gets in the way of seeing a clear image of the star through a telescope.
Light from stars is refracted through our atmosphere in different directions which causes the star’s image to change slightly in brightness and position. Even with a powerful telescope, factors like these make the stars difficult to see clearly. Enter adaptive optics in astronomy.

We can help you see far away objects more clearly
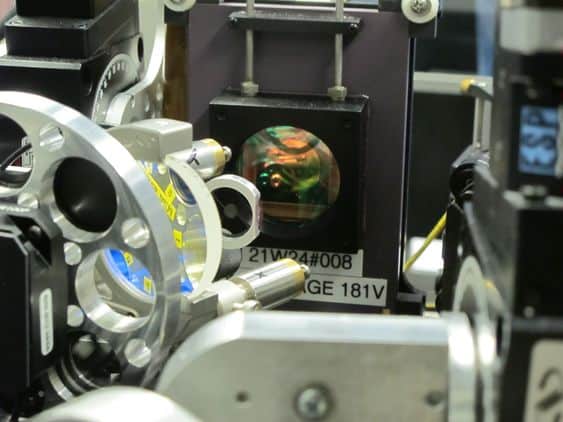
Our micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) deformable mirrors help telescopes compensate for atmospheric effects and correct for minor misalignments in instruments.
MEMS deformable mirrors have pistons underneath the surface that can move to change the mirror surface, effectively controlling the shape of the light reflected from it.
With the help of NASA SBIR programs and through internal development activities, BMC has developed new types of deformable mirrors and improved the cost of manufacturing deformable mirror hardware for adaptive optics in astronomy
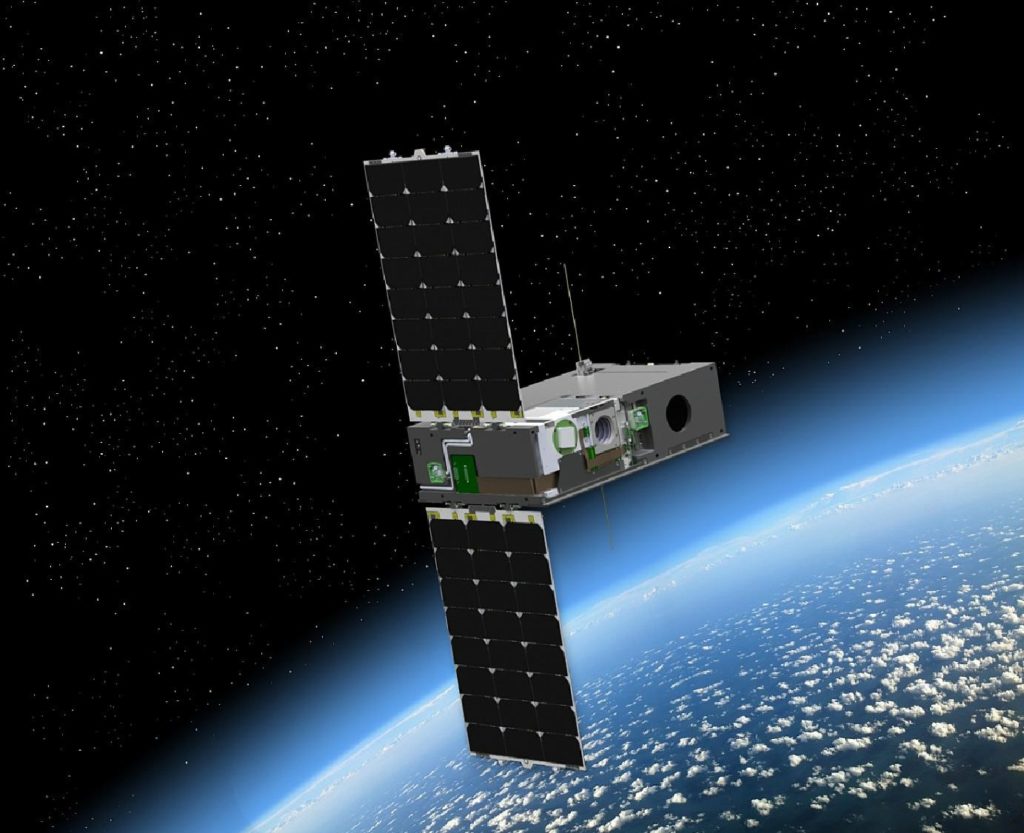
Boston Micromachines’ deformable mirrors are now being used in space telescopes and observatories around the world. These observatories are exploring the universe by imaging astronomical phenomena at resolutions previously unattainable due to the use of adaptive optics in astronomy.
How Adaptive Optics Improves Astronomy
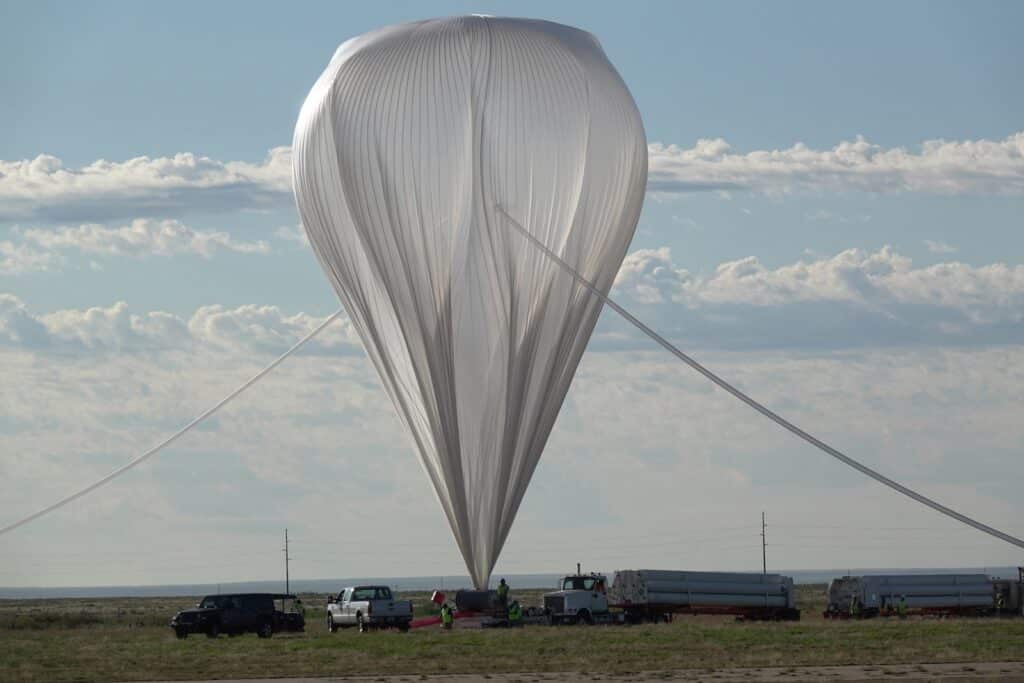
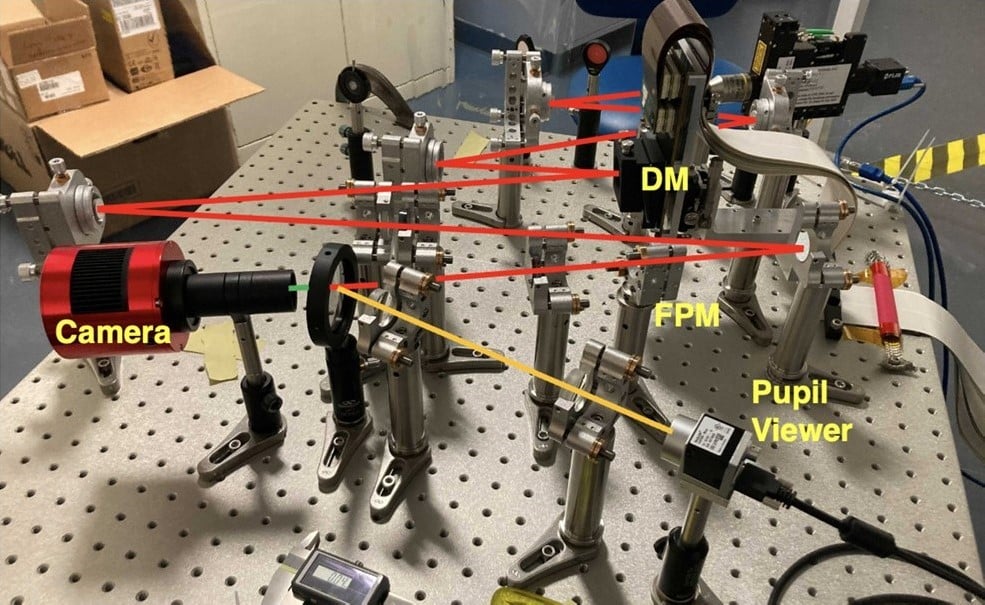
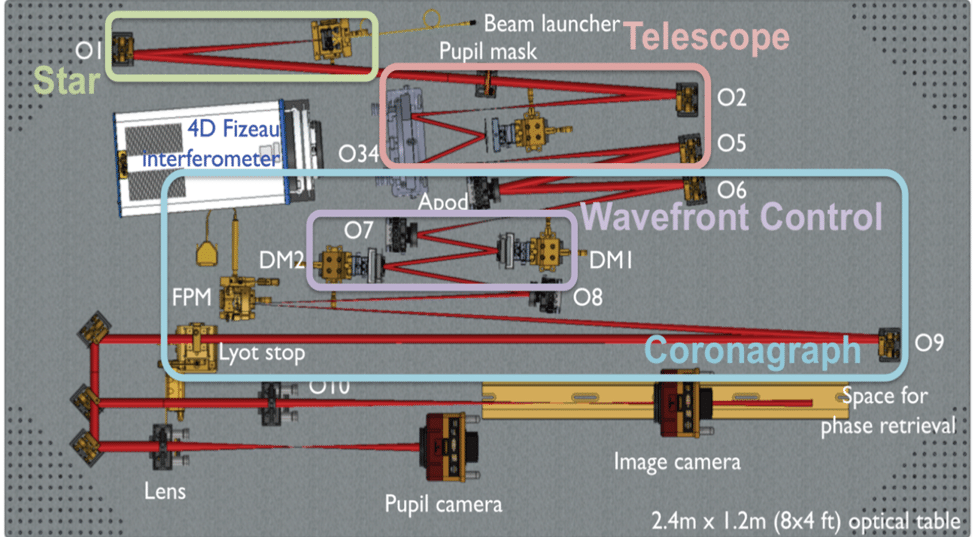
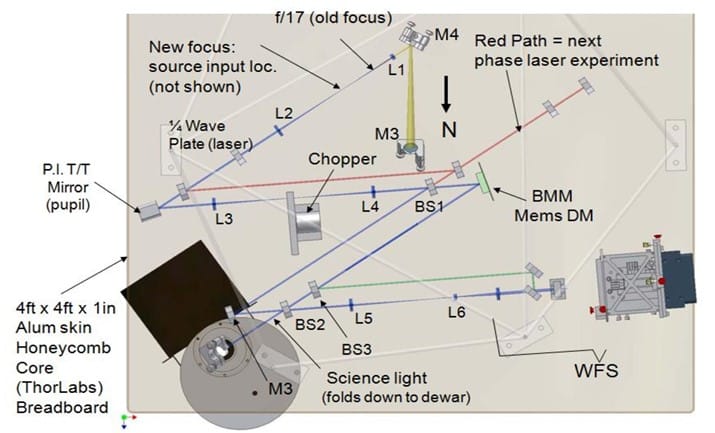
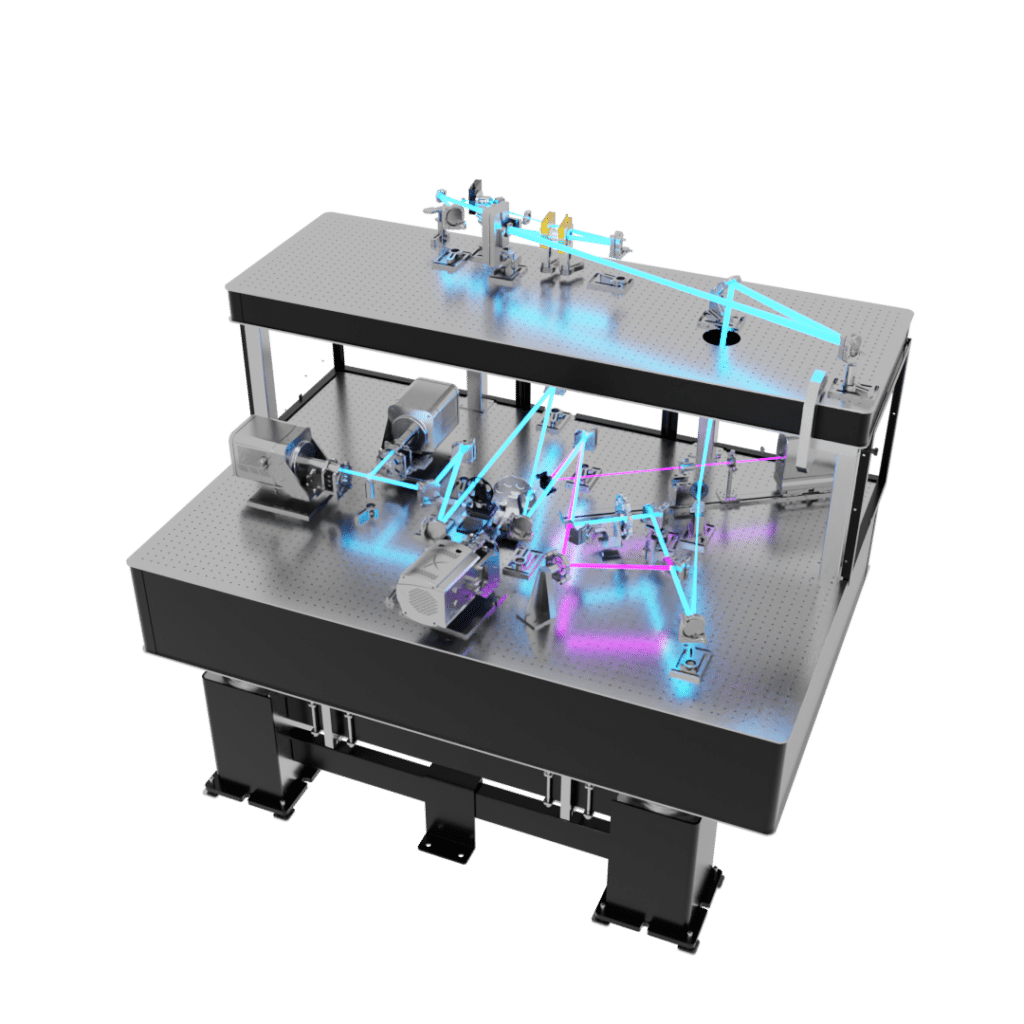
Optical Testbeds
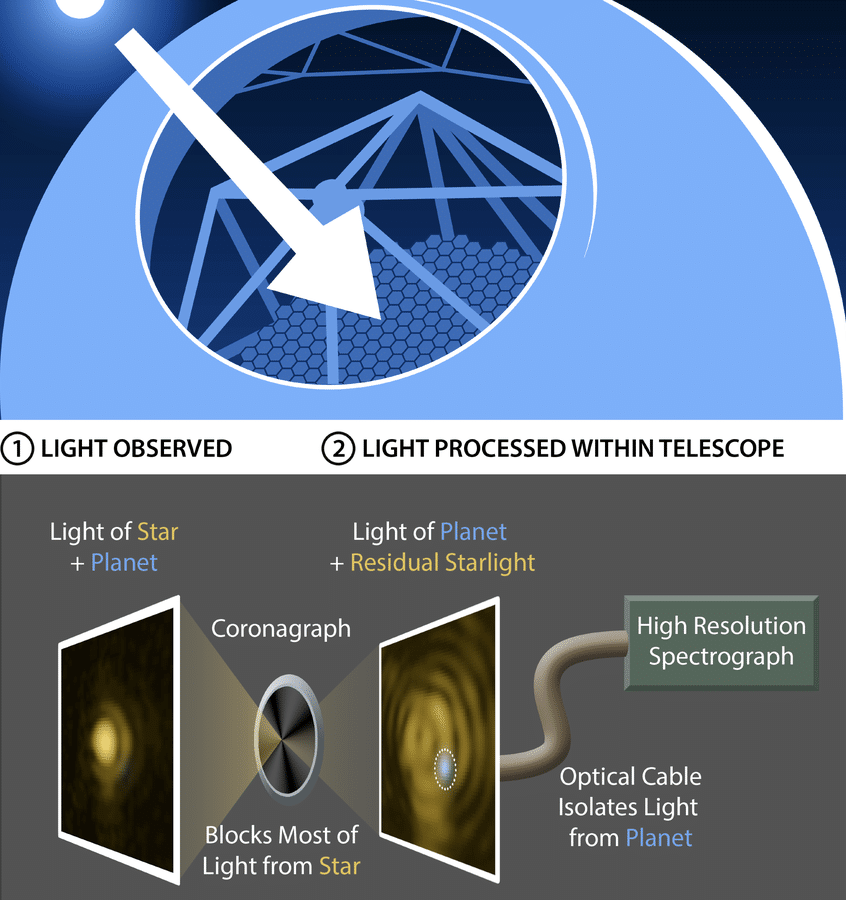
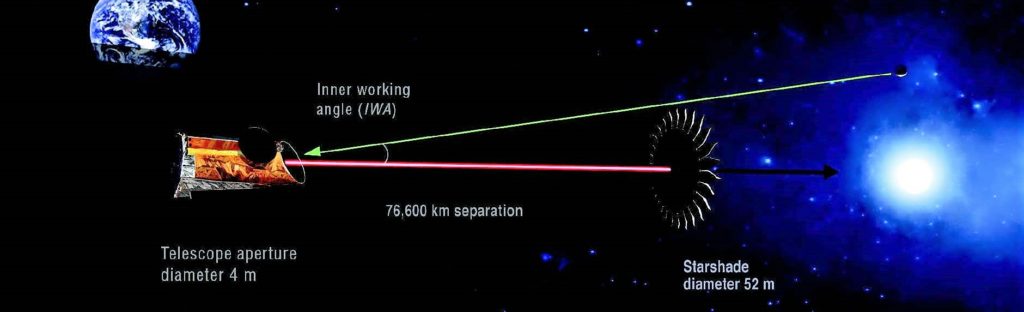
Exoplanet discovery using coronagraphy
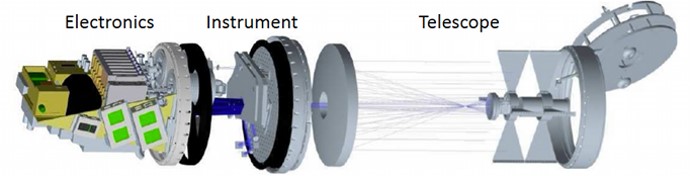
Space-based projects
Perform at a higher level with the latest technology
Boston Micromachines' continuous and segmented deformable mirrors are ideal for a range of applications in adaptive optics in astronomy.
BMC deformable mirrors enable sophisticated aberration compensation in an easy-to-use package.
Use a standard deformable mirror with an upgraded driver (X-Driver) to receive the fastest-in-class response time from your deformable mirror setup. With sizes ranging from 137 actuators to more than 4000 actuators, we are sure to have the right mirror for your installation.
In addition, the Boston Micromachines' Hex Class deformable mirror architecture can be used in testbeds to simulate the large segmented primary mirrors typically found in the latest Extremely Large Telescope designs. Hex mirror segments can tip, tilt and piston for alternative wavefront control.
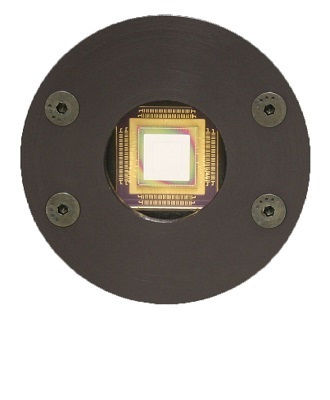
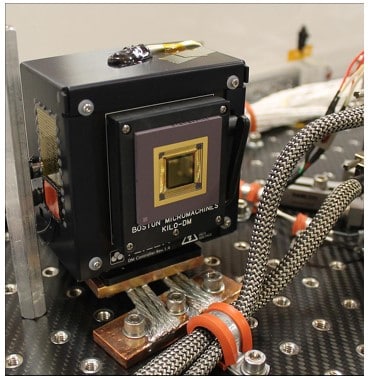
Standard Deformable Mirrors
Our deformable mirrors are fielded at prominent astronomical facilities around the world such as the Subaru Observatory and the Magellan Observatory to help researchers improve wavefront correction capabilities These deformable mirrors enable cutting edge space telescope concepts and are used in many facilities around the world. Learn more on the Standard Deformable Mirrors page.
Read more >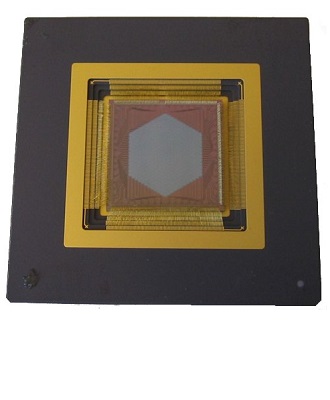
Hex Class Deformable Mirror
Hex deformable mirrors offer the ability to tip, tilt, and piston multiple segments in varous sized arrays. Boston Micromachines Hex DMs are in prominent astronomical testbeds around the world to help improve wavefront correction capabilities and can be used as primary mirror surrogates to test cutting edge telescope concepts. Learn more on the Hex Tip-Tilt-Piston page
Read more >Your desire for exploration shouldn't be hampered by wavefront aberrations. Let us help you choose the best deformable mirror for your system
so you can focus on moving your discovery forward with adaptive optics in astronomy. Contact us today.